
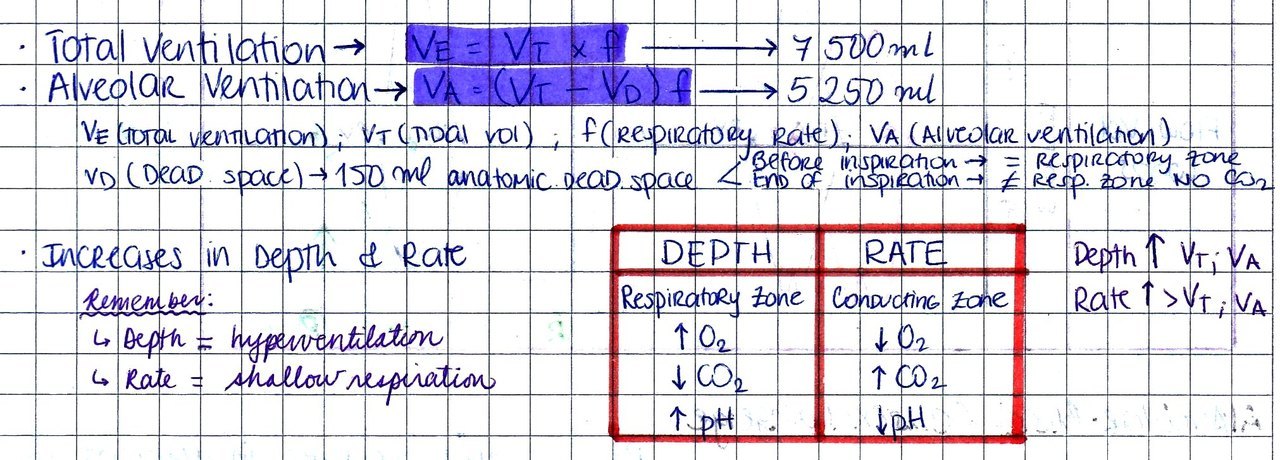
The physiologic dead space is the volume of inspired air that does not participate in gas exchange. Ventilation is the movement of air through the respiratory tract into (inspiration) and out of (expiration) the respiratory zone ( lungs ). edition. Saunders/Elsevier, 2010. ISBN 1416045740. Summary The main function of the respiratory system is gas exchange (O 2 and CO 2 ). Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology. 12. Minute Ventilation V ˙ Ventilation Values Measure.The ventilation can be divided into three categories according to the anatomical and functional properties of the lung airways: Usually it is measured in liters per minutes. However, differences in the exact way of measuring this space result in clinically significant different results and, therefore, debate remains about the true value of this measured parameter.Ĭopyright © 2023, StatPearls Publishing LLC.Is the called the amount of air entering the respiratory airways per unit time. Dead-space ventilation, the portion of a tidal volume that does not contribute to gas exchange, was first described and calculated by the Bohr equation in 1891, 1 and later by the Enghoff modification of the Bohr equation in 1938. Indeed, it may serve as a prognostic factor in patients with acute repository distress syndrome (ARDS) who require ventilation. This phenomenon has clinical significance because, both in healthy and impaired lungs, properly calculating and accounting for this non-physiological space is important for the proper respiratory care of ventilated patients. This is therefore termed anatomical dead space as it serves no respiratory function.
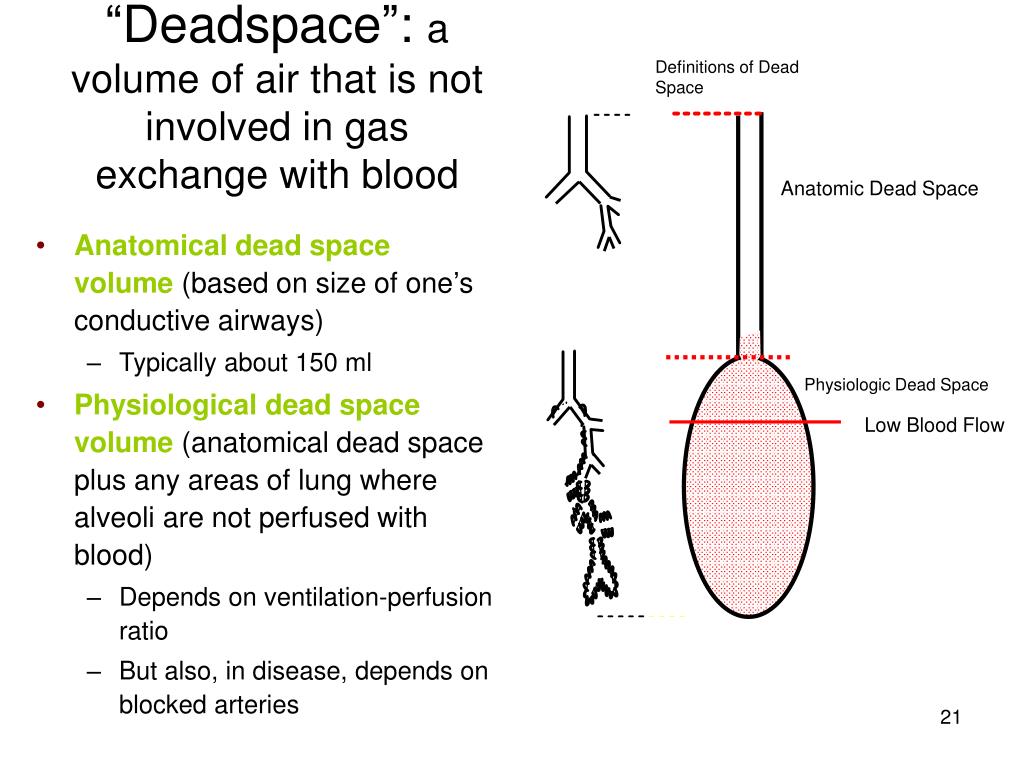
Anatomic dead space is an important phenomenon in respiratory physiology whereby, owing to the fact that upper airways do not function as locations for gas exchange, and because of the tidal nature of ventilation, there is always a fraction of the inspired air that does not perform a physiologic function of exchanging carbon dioxide for oxygen.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
